
Exploring the significance of a building envelope in roofing projects, this guide offers valuable insights to roofers looking to enhance energy efficiency and structural integrity. From discussing key components to sharing best practices, this comprehensive resource sets the stage for seamless integration and maintenance of the building envelope.
Importance of Building Envelope
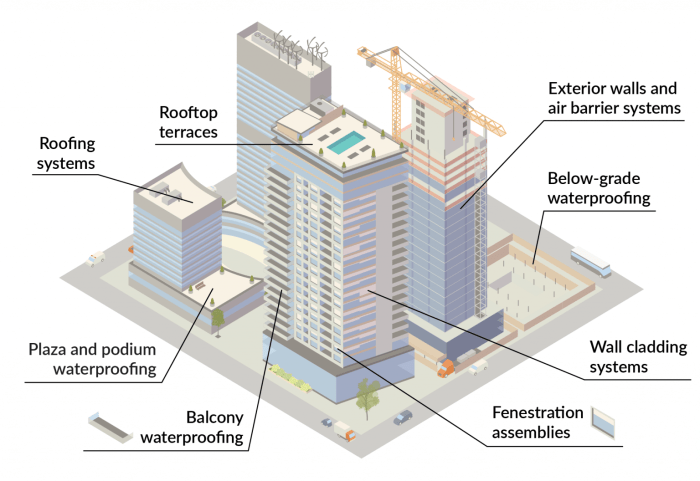
Building envelope plays a crucial role for roofers as it serves as the barrier between the interior and exterior environment of a structure. It includes the roof, walls, windows, and doors that help protect the building from elements such as rain, wind, and temperature fluctuations.
Contribution to Energy Efficiency
A well-designed building envelope is essential for energy efficiency in buildings. By properly insulating and sealing the envelope, heat loss or gain can be minimized, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. This not only helps in lowering energy bills but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly building.
- Insulation: Materials such as fiberglass, foam board, and spray foam are commonly used for insulating the building envelope. These materials help in maintaining a consistent indoor temperature by reducing heat transfer.
- Vapor Barrier: A vapor barrier is often installed to prevent moisture from entering the building envelope. This helps in avoiding issues such as mold growth and deterioration of building materials.
- Siding and Cladding: Materials like vinyl, wood, and fiber cement are frequently used for the exterior walls to protect the building from weather elements and enhance its aesthetic appeal.
Components of a Building Envelope
Building envelope components are crucial for the integrity and performance of a structure. Each element plays a specific role in protecting the building from external elements and ensuring energy efficiency. Let's explore the key components of a building envelope relevant to roofers and their functions within the system.
Roof
The roof is a critical component of the building envelope as it provides protection from weather elements such as rain, snow, and UV rays. It also contributes to energy efficiency by insulating the building and reducing heat loss.
Exterior Walls
Exterior walls form the perimeter of the building and are designed to resist wind, water, and temperature changes. They work in conjunction with the roof to create a barrier against external elements.
Windows and Doors
Windows and doors are openings in the building envelope that need to be properly sealed to prevent air and water infiltration. They play a role in natural light and ventilation while also impacting energy efficiency.
Insulation
Insulation is essential for regulating temperature within the building envelope. It helps maintain a comfortable indoor environment and reduces energy consumption by minimizing heat transfer through walls, roof, and floors.
Vapor Barrier
A vapor barrier is installed to control moisture levels within the building envelope. It prevents condensation and moisture buildup, which can lead to mold growth and structural damage.
Flashing
Flashing is used to redirect water away from vulnerable areas such as roof intersections, windows, and doors. It prevents water infiltration and protects these critical junctions from water damage.
Incorporating Building Envelope Design
When incorporating a building envelope into roofing projects, there are several key considerations to keep in mind to ensure a successful integration. The building envelope plays a crucial role in the overall performance and durability of the structure, so it is essential to approach the design process thoughtfully and strategically
Best Practices for Integration
- Coordinate with architects and engineers early on to align the building envelope design with the overall building structure and roofing system.
- Ensure proper insulation and air barrier installation to enhance energy efficiency and prevent moisture infiltration.
- Select materials that complement the roof system and provide long-lasting protection against weather elements.
- Integrate flashing details seamlessly to prevent water penetration at critical junctions between the roof and building envelope.
- Consider incorporating sustainable design elements to improve the building's environmental performance and reduce long-term maintenance costs.
Addressing Potential Challenges
- Identify and mitigate any potential conflicts between the roofing system and building envelope early in the design phase to avoid costly rework later on.
- Account for thermal movements and structural loads to ensure that the building envelope can accommodate the roof system without compromising its integrity.
- Collaborate closely with contractors and subcontractors during the implementation phase to address any unforeseen challenges and ensure a smooth and efficient construction process.
Maintenance and Repair of Building Envelope
Regular maintenance and timely repairs are crucial for ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of a building envelope. By addressing issues promptly, you can prevent costly damage and maintain the structural integrity of the building.
Essential Maintenance Tasks
- Inspecting the building envelope regularly for signs of wear and tear, such as cracks, leaks, or gaps.
- Clearing debris from gutters, downspouts, and roof drains to prevent water accumulation and potential water damage.
- Checking for proper insulation and sealing to enhance energy efficiency and prevent air leakage.
Identifying Common Issues
- Water infiltration through cracks or gaps in the building envelope.
- Deterioration of sealants or weather-stripping that can compromise the envelope's integrity.
- Damage to roofing materials, such as shingles or membranes, leading to leaks and moisture intrusion.
Repair and Restoration Techniques
It is essential to address any issues with the building envelope promptly to prevent further damage and maintain the building's structural integrity.
- Sealing cracks and gaps with appropriate sealants to prevent water infiltration.
- Replacing damaged or worn-out roofing materials to prevent leaks.
- Repairing or replacing weather-stripping and sealants to maintain the envelope's tight seal.
Closure
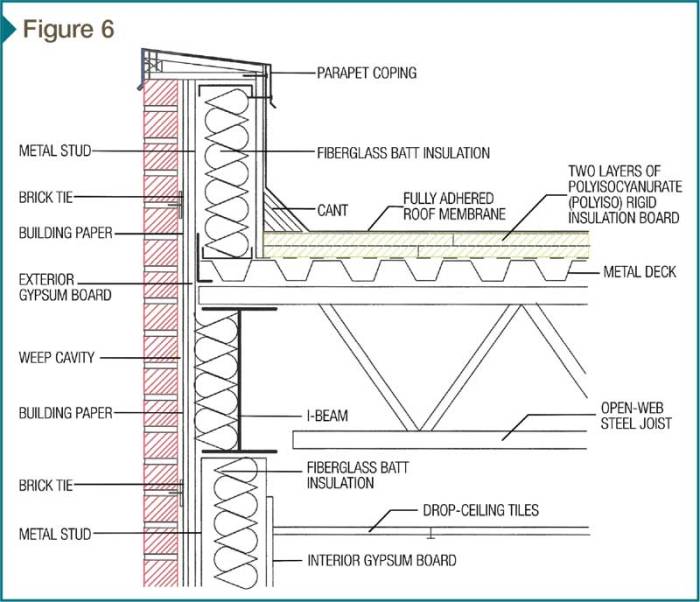
In conclusion, mastering the art of incorporating a building envelope is crucial for roofers seeking to elevate their craft. By understanding the design considerations, maintenance tasks, and repair techniques Artikeld in this guide, roofers can ensure long-lasting and efficient roofing projects.
Essential Questionnaire
How does a well-designed building envelope contribute to energy efficiency?
A well-designed building envelope acts as a barrier against heat transfer, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling, thus improving energy efficiency.
What are the common materials used in building envelopes for roofing projects?
Common materials include asphalt shingles, metal roofing, clay tiles, and slate, each offering unique benefits in terms of durability and aesthetics.
What are some best practices for integrating the building envelope seamlessly with the roof?
Ensuring proper flashing installation, using compatible materials, and maintaining a watertight seal are key best practices for seamless integration.
How can roofers identify common issues with the building envelope?
Roofers can look out for signs of water damage, mold growth, or air leaks as indicators of potential issues with the building envelope.










